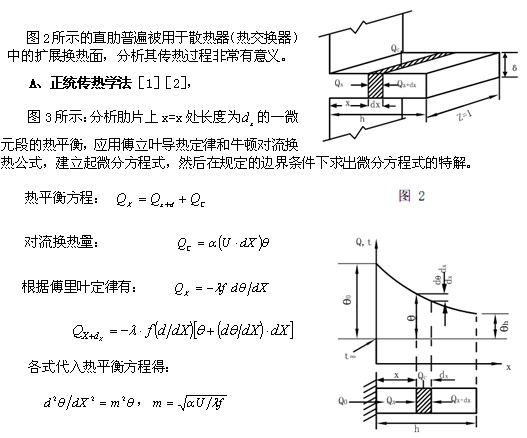
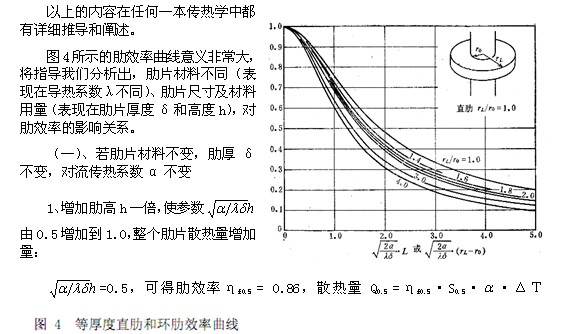
I. Introduction
Due to its power saving, environmental protection and long life, LED is recognized as the next generation of human lighting technology. The biggest obstacle to the popularization of LED lighting applications is the high price of LED lamps, and the high price is caused by heat dissipation.
Heat dissipation is part of heat transfer. Humans have studied heat transfer for hundreds of years. In the 1960s and 1970s, people were at the peak of heat transfer research. The main driving force was the demand for human aerospace development. At that time, many outstanding talents gathered in the field of heat transfer technology, and many well-known people. With the increasing maturity of heat transfer technology and technology, people's enthusiasm for heat transfer research is gradually decreasing. Currently, professionals in heat transfer and technology are very Less, heat transfer and technology are very mature, like a ripe fruit, falling to the ground and covered by leaves, not seen by the present people.
In the heat dissipation of LED, the temperature is not high (not exceeding 100 °C), it is a complex process such as normal temperature heat transfer, no phase change, and the power is not large. The single LED chip is also 1~2W, in terms of heat transfer and technology, LED heat dissipation is very simple and involves only a very small part of heat transfer—thermal heat transfer and convective heat transfer (mainly air convection heat transfer), where heat transfer and heat transfer can be achieved using off-the-shelf heat transfer computer software. The exact solution.
The reasons for the simple problem of LED heat dissipation are complicated: knowledge faults, people with mature heat transfer knowledge participate in LED heat dissipation research, people do not pull the leaves on the ground, pick up those ripe fruits To transplant human mature heat transfer knowledge into the electronics industry, but to re-breed and plant trees.
The heat transfer in the LED industry (or the electronics industry) can be said to be another stove. The new terms created by the industry: "active heat dissipation" and "passive heat dissipation" can illustrate this point. There is also the term "heat sink" which is very familiar in the industry. It doesn't sound like what it means. English "Sink" is also a very rare term in heat transfer technology and technology. The following mature heat transfer is called "orthodox heat transfer", and the heat transfer in the LED industry (electronic industry) is called "industry heat transfer", the problem and concept of analysis of industry heat transfer Inconsistent with orthodox heat transfer, this article will analyze the application of the concept of "thermal resistance" in the industry, the problem of heat transfer in the LED industry.
The concept of "thermal resistance" has been abused in the industry heat transfer science, which clearly shows the brand of "electronic circuit science", which decomposes the whole LED heat dissipation process into series and parallel connection of several "thermal resistance" components, as shown in Figure 1. The thermal resistance analysis of the LED heat dissipation process is very common in the LED industry, just like the resistance in a circuit.
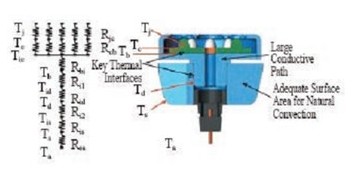
Figure 1
In an electronic circuit, the resistance in the series circuit is not divided before and after; the resistance in the parallel circuit is not divided, but the heat transfer process is not the case. In the electronic circuit: the series-parallel relationship of the resistor is very clear, the resistance value of the resistor is basically artificially set, or can be directly measured or derived by the instrument. However, in the heat transfer process, especially in the heat dissipation process of the LED, there is no clear and clear thermal resistance series-parallel relationship, and the thermal resistance value cannot be simply calculated. If the "thermal resistance" method is used to calculate and analyze, the simple problem will be solved. complication. The concept of "thermal resistance" is rarely used in orthodox heat transfer to analyze the heat transfer process.
The following is further illustrated by two examples of analysis and comparison.
Second, the "thermal resistance method" and the orthodox heat transfer method comparison