According to the characteristics of the Lambertian light source, define the near Lambertian light source function, design the optical model of the LED lens, obtain the cross-sectional curve equation of the LED, use the Runge Kuta method to solve the equation, and use polynomial fitting in MATLAB to obtain the relevant data and correction After the data, through Tracepro simulation to obtain the desired LED near Lambertian light source packaging model data and simulation results. A simplified design method of LED near Lambertian light source optical model packaging is proposed.
Lambertian light source is a light source widely existing in nature. The sun, frosted glass lampshade, snow and white wall can be regarded as Lambertian light sources. The LED chip itself is a Lambertian light source. The luminous beam angle 2θ1 / 2 is 120 °. Due to the large beam angle, the luminous intensity is low, and the early photoelectric conversion efficiency of the chip is also low. In order to obtain greater light intensity, it is necessary The optical structure of the package lens of the LED is designed to control the light beam angle of the LED and concentrate its beam in a certain direction, so LED devices with different beam angles such as 120 °, 90 °, 60 °, and 30 ° appear. The LED Lambertian light source with a beam angle of 120 ° is isotropic, which is an ideal light type. Corresponding to other LED devices that emit light beam angles, they are usually designed as packaged optical lenses near Lambertian light sources in order to obtain a better light-emitting type.
At present, LED technology is developing rapidly, and the lumen luminous efficiency of high-power LED devices has reached a relatively high level of 100 lm / W. These LED devices with different beam angles are used as local directional signals or illumination light sources. Their application is flexible and selective, but their cost performance is still high. The design and application of near-Lambertian light source devices can reduce the number of LEDs, increase energy-saving effects, reduce engineering cost, and improve the application level of LED semiconductor light sources.
1. Lambertian light source
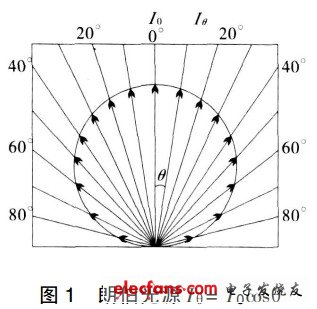
In photometry, the luminous intensity Iθ of a Lambertian light source in a certain direction is equal to the luminous intensity Io in the vertical direction of the light emitting surface of the light source multiplied by the cosine of the direction angle. As shown in FIG. 1, the Lambertian body is also called a cosine emitter. Bo light source is also called cosine body light source. The intensity of the Lambertian light source in the direction of θ is
Iθ = Iocosθ
Shaoxing Tianlong Tin Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.tianlongspray.com