Reliability refers to the ability of a product to perform a specified function under specified conditions and within a specified time. Reliability is a measure of the ability to work without failure when a product is put into service. The level of product reliability is the size of the product under the specified conditions and within the specified time. Reliability is usually expressed by reliability, failure rate and MTBF. The reliability level of components such as sensors is usually expressed by failure rate, and the reliability of equipment is represented by indicators such as reliability, MTBF, and effectiveness.
Pressure is one of the most basic parameters for measurement and control in production processes and scientific experiments. Pressure sensors that measure pressure and convert pressure into electrical signals through certain laws become important components for measuring this signal. It is widely used in the production and research of industrial, petroleum, chemical, biomedical, marine, aerospace, aviation and other fields. The reliability of the sensor is very important. It is directly related to the performance of the system using the sensor, affecting the quality and speed of production and construction, and even causing serious personal safety problems. In the use of the sensor, its reliability concept can be used as a non-faulty property, that is, as a performance total for ensuring the use index of the limit required by the technical conditions. When a sensor that transforms a specific physical quantity fails, it can be understood that the component that destroys the mechanical integrity of the component and the deviation of the output measurement parameter causes the entire product of the sensor to fail to complete the task. In the production process of the sensor, in order to ensure the accuracy, stability and consistency of the pressure sensor's measurement and transmission of the pressure signal, the reliability of the test process of the pressure sensor must be analyzed.
2 Pressure sensor test principleThe pressure sensor includes a piezoresistive pressure sensor fabricated by piezoresistive effect, a piezoelectric pressure sensor fabricated by piezoelectric effect, a strain gauge pressure sensor manufactured by strain effect, etc., and only a piezoresistive pressure sensor is taken as an example herein. , explain its testing principle.
The core of the piezoresistive pressure sensor is shown in Figure 1. R1, R2, R3, and R4 are four resistors. When subjected to external force, the resistors R1 and R3 are also subjected to tensile resistance increase, and R2 and R4 are reduced. Therefore, the action of the external force F changes the resistance values ​​of the four resistor sheets. The resistors R1, R2, B3, and R4 on the sensor are connected to the DC bridge shown in Figure 2. The cd is connected to the regulated power supply E at both ends, and the two ends are the bridge voltage output terminals, and the output voltage is U0, as shown in Figure 2.
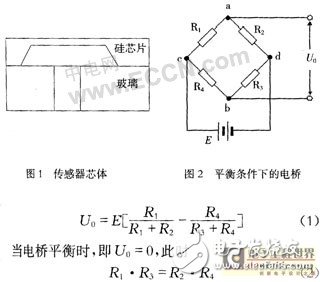
Equation (2) is the bridge balance condition. The resistors attached to the sensor are the same four resistors. Under ideal conditions, the resistance values ​​are the same, that is,
R1=R2=R3=R4=R (3)
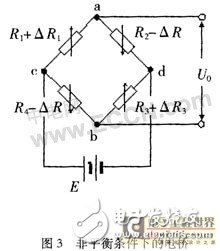
Therefore, when the sensor is not subjected to an external force, the bridge satisfies the equilibrium condition, and the voltage U0=0 outputted at both ends of a and b. When the beam is subjected to the load F, as shown in Figure 3, the bridge is unbalanced, then there is

It can be seen from equation (6) that the unbalanced voltage U0 of the bridge output is proportional to the change ΔR of the resistance, which is the working principle of the unbalanced bridge. Obviously, the measured size of U0 can reflect the magnitude of the external force F. In addition, it can be seen from equation (6) that if a larger output voltage U0 is to be obtained, a higher power supply voltage E can be used, and it is also indicated that the instability of the power supply voltage will bring errors to the measurement results. In the actual production test process, the four resistors of the bridge arm are not exactly the same, and the environmental conditions added during the test also affect the output of the sensor. Thus, when the environmental conditions change, their increments ΔR are also not identical, which ultimately leads to deviations between the test results and the desired results.
The test of the pressure sensor mainly refers to the temperature output characteristic test and the pressure output characteristic test. The temperature output characteristic test mainly refers to the influence of the pressure sensor on the sensor output under different temperature conditions, mainly refers to zero temperature drift and sensitivity temperature drift; the pressure output characteristic means that the pressure is reflected by different pressures under the same environmental conditions of the sensor. The output characteristics, which are mainly used to measure the static characteristics of the sensor.
The pressure sensor measurement system is mainly composed of four parts: the pressure source, the tested pressure sensor, the measuring circuit and the display record. Their relationship is shown in Fig. 4.
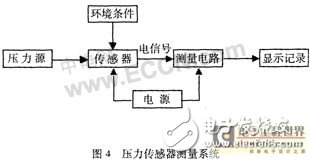
The pressure sensor to be tested is measured under certain environmental conditions (provided by the high and low temperature environmental test chamber) and supplied by the power source, and the signal generated by the pressure source (piston pressure gauge or digital pressure controller) is measured. The signal is finally transmitted to a display device (computer) for display and recording through a measurement circuit (multi-channel data collector).
4 Factors that affect the reliability of the pressure sensor test equipment during the testThe reliability indicators of the pressure sensor test process are constantly changing as the design is modified, the conditions of use are different, and the performance degradation during the work process. Therefore, it must be considered in many aspects.
4.1 Conditions for use
Any product development is carried out according to the specified conditions of use. This conditions of use include operating conditions (such as functional mode, mode of operation, load conditions, operating energy, maintenance conditions, etc.) and environmental conditions (such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, vibration, etc.). The reliability of the same product is different under different working conditions and environmental conditions. Equipment that tests pressure sensors is no exception.
The environmental conditions that affect the reliability of the test process generally include the following: climatic environmental conditions, mechanical environmental conditions, biological conditions, chemical conditions, electrical and electromagnetic conditions, radiation conditions, system connection conditions, and human factors. The main considerations are climate environmental conditions, chemical conditions and system connection conditions. The climatic and environmental conditions include temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind, rain, frost and sand. Chemical conditions include factors such as power supply instability, interference signals from conductive line systems, interference from electromagnetic fields, and lightning, corona and discharge. The system connection conditions include factors between the functional units in the large system, and one system or one device is connected to other devices. The above three factors have an impact on the reliability of the equipment, but the degree of influence of various factors on different equipment is different.
4.2 Time of use
The reliability of the sensor test equipment is a function of time, which decreases with time. Even if the components are screened and the machine is tempered and repaired, and the equipment works in the accidental failure zone, the failure in this period of time The rate is a constant. However, the distribution law of the device with time is in accordance with the law shown in Figure 5, that is, the longer the use time, the lower the reliability of the test equipment.
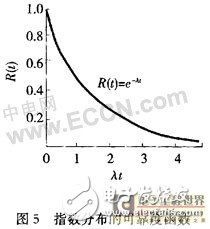
4.3 What can be achieved
The so-called "function" is the main performance indicators and technical requirements of the product. This is the guarantee that the product fulfills the specified tasks and functions. The so-called product is not reliable, it is sufficient for the product to meet the specified performance indicators and technical requirements. The higher the performance index and technical requirements of the product, the smaller the allowable range of variation, the less likely the product is to complete the “specified functionâ€, and the lower the reliability level of the product. Conversely, the lower the performance and technical requirements of the product, the wider the range of changes allowed, and the greater the likelihood that the product will be able to perform the “specified functionâ€, and the higher the level of reliability of the product. For the test equipment of the sensor, the higher the test accuracy requirement of the sensor, the lower the reliability level, but the more realistic the data of the sensor can be measured by the test equipment. Conversely, if the test accuracy requirements of the pressure sensor are lower, the reliability level of the device is higher, but the influence on the real data of the sensor is greater.
It should also be pointed out that from the perspective of the use of test equipment, the most important indicator of the equipment is the reliability index under the premise that the basic performance indicators meet the requirements of use. If the device is unreliable, the performance is unstable, and it is often bad, the initial performance of the test device is no longer practical, let alone the actual data of the sensor.
4.4 Reliability Analysis
It is assumed that under a certain confidence value, the reliability of the pressure source is R1(t), the reliability of the environment providing equipment is R2(t), the reliability of the measuring circuit is R3(t), and the reliability of the power supply system is R4. (t), then the reliability R(t) of obtaining the real data of the sensor is necessarily related to R1(t), R2(t), R3(t), R4(t), ie
R(t)=f[R1(t), R2(t), R3(t), R4(t)] (7)
It is known from the measurement system of equation (7) and FIG.
R(t)=K? R1(t)? R2(t)? R3(t)? R4(t) (8)
In the formula, K is a coefficient, which is closely related to the use time and use conditions of various devices.
Now, using the sensor test of my unit, the test of the pressure sensor is not taken as an example: under the same test conditions, the zero temperature test is performed on 10 uncompensated pressure sensors using two different environmental devices. The parameters of the two ovens are shown in Table 1. The test data of the sensors are shown in Table 2.
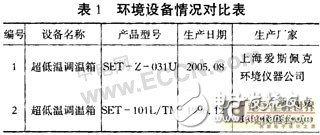
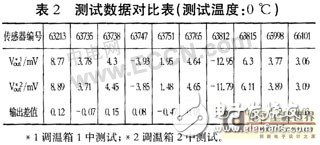
The data in Table 2 shows that the test results are different when using other thermostats under the same conditions, and the most important thing for us is to determine which group of data is more reliable and closer. Real data on sensor performance. It can be seen from Table 1 that the 1# thermostat box has been working for nearly two years, and the 2# withered tank has been working for more than ten years. According to the distribution law of equipment reliability with time, the reliability of No. 1 equipment is higher than that of 2# equipment. Sex. Therefore, the sensor data measured with the 1# device is more reliable.
4.5 Measures to increase the reliability of the test process
1 Strengthen the management of pressure sensor test equipment, regular maintenance and maintenance, and improve the service life of equipment based on the performance requirements.
2 Strictly control the environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity and cleanliness of the test site; shorten the turnaround time between processes and improve the test efficiency of the sensor.
3 Regularly test and calibrate various verification equipments to ensure that the performance of the test equipment meets the requirements for sensor testing, and thus ensure the reliability of the test data obtained.
4 Adhere to the summary, calculation and analysis of the sensor test data, find out the factors affecting the sensor output during the test process, and solve it, laying a solid foundation for improving the quality of the sensor products.
5 ConclusionBased on the reliability of pressure sensor, the concept of reliability of pressure sensor test process is put forward, and the factors affecting the output of pressure sensor during the test process are expounded. The measures to increase the reliability of sensor test process are proposed. Provide a new idea for in-depth study of pressure sensors.
Lithium Battery 2Cr11108,Marine Lithium Battery,Lithium Battery Smoke Alarms,Manganese Dioxide Lithium Battery
Jiangmen Hongli Energy Co.ltd , https://www.honglienergy.com