The realization of burst aggregation
2.1 Establishment of GMPLS LSP
There are two signaling protocols for GMPLS (Constraint-based Routed Label DistribuTIon Protocol, CR-LDP) and (Resource ReservaTIon Protocol-Traffic Engineering, RSVP-TE). This article takes CR-LDP as an example. In FIG. 3, the edge node A judges that the LSP from A to I is to be established, and then knows to establish the LSP of A, B, H, and I through some flow information or network management information. A sends a request message (label request) to B, which contains the display path (B, H, I) and other information, such as forwarding equivalent FEC, LSP identification, optional traffic engineering information, and LSP priority information, etc. Therefore, once the LSP is established, it may itself contain priority and traffic engineering information. B receives the request message, sends the request message along the path specified by the message, and changes the display path to (H, I). The operation of H is similar to the operation of B above. I receives the request message and judges that it is the exit of the LSP. For this reason, the LSP reserves resources, allocates tags, establishes a forwarding table, and sends the tags to H through a response message (mapping request). H receives the response message, matches the original request with the LSP ID contained in the request message and the response message, assigns a label, establishes a forwarding table, and sends the new label to B through the response message. The operation of B is similar to the operation of H above. The operation of A is also similar to the operation of H above, except that it does not need to be forwarded with a newly allocated label.
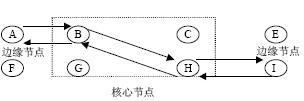 Figure 3 Establishment of LSP
Figure 3 Establishment of LSP
2.2 LSP aggregation and burst aggregation
LSP aggregation means that the upper layer LSP can be aggregated to the lower layer LSP [4], that is, the IP packet LSP can be aggregated to the time division multiplexing (TIme Division MulTIplexing, TDM) LSP. Converged to optical fiber LSP. Burst aggregation is the aggregation of data packets from the same edge node to the same destination edge source node. In OBS, the edge node generally receives IP data packets, and the core node is the dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) of the optical path. Therefore, GMPLS is applied in OBS to converge the LSP of IP data packets to the optical layer LSP is completely feasible, the specific implementation process is shown in Figure 4.
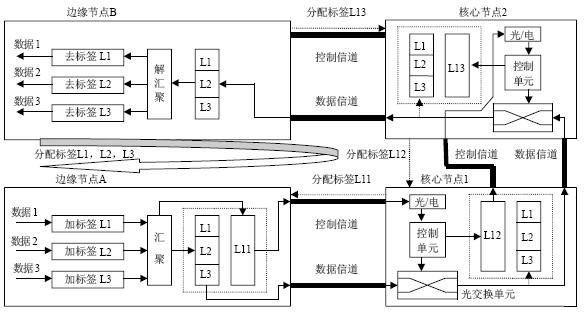
Figure 4 Implementation of burst aggregation In Figure 4, L1, L2, and L3 are the packet switching labels assigned by edge node B to edge node A when establishing a packet LSP through the GMPLS signaling protocol. They respectively imply the following LSP, namely (L1 , L11, L12, L13), (L2, L11, L12, L13) and (L3, L11, L12, L13). For the sake of simplicity, the label is used here to represent all LSP information. L11 is the wavelength exchange label assigned by the core node 1 to the edge node A, implying a wavelength LSP (L11, L12, L13); L12 is the label assigned by the core node 2 to the core node 1, L13 is the edge node B assigned to the core The label of node 2. At edge node A, when IP packets (data 1, data 2, data 3) arrive, add packet labels L1, L2, L3 to them respectively, and the edge node finds that they are all to the same destination edge node according to the LSP information Go to B, and then gather them by the LSP information of the optical layer. According to the rule of burst aggregation [5], after reaching the maximum length or maximum time, add the label L11 to the BHP of the burst packet and send it to the core node 1. After waiting for the offset time, L1, L2, and L3 are transferred to the core node 1 together with the data. The label aggregation in Figure 4 is drawn together for intuitiveness, and the general LSP aggregation uses a label stack. But in the optical burst, the control information and data of the optical layer are transmitted separately, there is no need to use the label stack, just send the original stack top label to the BHP. The core node 1 knows that the data should be sent to the core node 2 according to the label forwarding table and the received label in the BHP, then turns on the corresponding optical switch, and at the same time changes the label in the BHP to L12 and sends it to the core node 2, then The incoming data is also sent directly to the core node 2. The data processing of the core node 2 is similar to the core node 1. When the data arrives at the edge node B, B judges that it is the terminal of the optical layer LSP, then releases the received burst packet, and then determines the destination of the data and sends it according to the packet switching label allocation table of the IP layer.
2.3 Change of label allocation table and label The first condition for achieving burst aggregation is that the data goes to the same edge node. In the traditional label allocation table, only the address prefix, label, and port information of the destination node are used. Therefore, using the usual label allocation table is Unable to complete the gathering. The edge node of the GMPLS-based OBS network is the starting point of source routing (GMPLS uses source routing). The edge node has sufficient network topology information, so that an item of information is added to the label allocation table, that is, the destination edge node corresponding to the label Address prefix. When converging, according to the modified label allocation table, as long as you know the label and the outgoing port, you can know the destination edge node of the data, and then according to other information such as priority, the data can be aggregated to the burst packet that should go.
When the burst aggregation group packet is completed, one is that the time reaches the required value, and the other is that the length reaches the required value. In GMPLS, the packet information comes from the label, and the traditional label mainly completes the data exchange, does not contain the length information of the packet, so the label (IP layer label) needs to add a piece of length information, so that the length information is easily obtained during aggregation To complete the gathering.
In order to accurately determine the offset time, the response message (Mapping Request) must be modified when the LSP is established, and a time for the node to process the BHP is added. In this way, the edge node only needs to add this item to get a comparison. Accurate offset time.
3 Traffic engineering and data recovery and protection [6,7]
In the GMPLS-based OBS, the establishment of the GMPLS display routing LSP at the edge node is used to control the direction of service traffic, and the extended Open Shortest Path First (OSFP) protocol is also required to obtain more network resources Information, including wavelengths in optical networks and even the status of optical fibers, supports rapid exchange of flows of different granularity levels and efficient traffic engineering. Traffic engineering generally has two implementation methods: online mode and offline mode. Online mode uses routing / signaling protocols to implement online path calculation through a limited routing algorithm; offline mode considers the realization of traffic engineering from the optimization of the entire network resource usage . The offline mode is a long-term solution for the overall optimization of network resources; the online mode only considers a subset of resources, and it can dynamically follow traffic changes. An effective traffic engineering strategy must meet the two necessary conditions of responding to short-term traffic changes and optimizing the use of network resources, that is, responding to short-term traffic changes and optimizing the use of network resources. Therefore, a good solution is a combination of the two, that is, to achieve long-term (eg, daily, weekly) overall optimization through offline mode; and between the two overall optimization can be achieved online Local optimization.
Data recovery and protection are accomplished using GMPLS signaling protocol (RSVP-TE or CR-LDP) and link management layer protocol. Recovery and protection are divided into multiplex section layer protection and channel layer protection. The protection and restoration of the multiplex section layer is generally provided on the link between two adjacent nodes, while the protection and restoration of the channel layer is provided on one optical path, which can be composed of several network nodes.
It can be seen from the above that OBS based on GMPLS is not only feasible, but also provides a unified management plane for the network, which makes the network have good scalability and network management has become very simple. At the same time, GMPLS-based OBS not only provides better offset time settings, traffic engineering, and data recovery and protection, but also has the following advantages:
1) Since GMPLS implements display routing, it is easy to perform constraint-based QoS algorithms, and the LSP itself can also contain priority information, so various levels of QoS can be achieved.
2) Because each layer uses unified signaling, it can control each layer uniformly. Therefore, as long as it is on the same GMPLS network interface, the virtual private network (Virtual Private Network, VPN) function can be provided to the client terminal device, which reduces the configuration burden of the connection between the client devices and provides connection security.
GMPLS-based OBS has the common advantages of OBS and GMPSL, which is in line with the development trend of communication networks.
Research on Optical Burst Switching Based on GMPLS
Selecting a table lamp that is right for your room is important for both the lighting and overall design of your home. Table lamps can help you add ambient lighting to your living space and complement your existing decorate and accent setup. A table lamp is a beautiful way to freshen up your existing décor and add new textures to your living space. Table lamps rest on all furniture types and can essentially go into any room in your home such as the living room, bedroom, or office.
A table lamp in the living room should match the furniture color. You also might want to think of the color of your floor or rugs. For example, a white lamp in a room with lighter hues can fit into the room nicely. A tan colored rug could match a black lamp well too. You should avoid bolder colors if you don't want the table lamp to be too eye catching. For the bedroom, the lamp is likely going on the nightstand next to your bed. You want an option that is easy to turn off and on and gives off enough light. To find the perfect table lamp for your office, consider where it will go in the office. It will likely sit atop a desk by your computer. To avoid a cluttered desk, you should pick a smaller option. If it's going on a small accent table next to your desk, then a larger one can definitely work.
LED Touch Table Lamp With USB Port
LED Touch Table Lamp With USB Port,Touch Table Lamp
Shenzhen Superlight Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.superlighttech.com