1. The basic composition of the phase-locked loop
Many electronic devices need to work normally, usually requiring an external input signal to be synchronized with the internal oscillating signal. This can be achieved by using a phase-locked loop.
The phase-locked loop is a feedback control circuit, referred to as a phase-locked loop (PLL). The phase-locked loop is characterized by the use of an externally input reference signal to control the frequency and phase of the internal oscillating signal of the loop.
Since the phase-locked loop can automatically track the input signal frequency to the input signal frequency, the phase-locked loop is usually used for the closed-loop tracking circuit. During the operation of the phase-locked loop, when the frequency of the output signal is equal to the frequency of the input signal, the output voltage maintains a fixed phase difference with the input voltage, that is, the phase of the output voltage and the input voltage is locked, which is the phase lock. The origin of the ring name.
Typically the phase detector PLL (the PD), a loop filter (LF) and a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) of three parts, consisting of a phase locked loop block diagram shown in Figure 8-4-1.
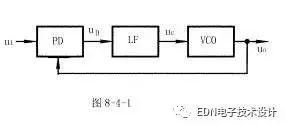
The phase detector in the phase-locked loop is also called phase comparator, and its function is to detect the phase difference between the input signal and the output signal, and convert the detected phase difference signal into a uD(t) voltage signal output. After the low pass filter is filtered, the control voltage uC(t) of the voltage controlled oscillator is formed, and the frequency of the oscillator output signal is controlled.
2. The working principle of the phase locked loop
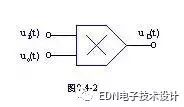
The phase detector in the phase-locked loop is usually composed of an analog multiplier, and the phase detector circuit composed of the analog multiplier is shown in Figure 8-4-2.
The working principle of the phase detector is to set the signal voltage input by the outside world and the signal voltage output by the voltage controlled oscillator to be:
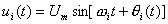
(8-4-1)
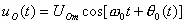
(8-4-2)
The ω0 in the equation is the oscillation angular frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator when the input control voltage is zero or DC voltage, and is called the natural oscillation angular frequency of the circuit. Then the output voltage uD of the analog multiplier is:
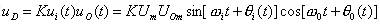
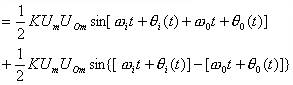
The sum frequency component in the above equation is filtered out by the low pass filter LF, and the remaining difference frequency component is used as the input control voltage uC(t) of the voltage controlled oscillator. That is, uC(t) is:
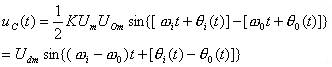
(8-4-3)
The ωi in the equation is the instantaneous oscillation angular frequency of the input signal, and θi(t) and θO(t) are the instantaneous phases of the input signal and the output signal, respectively. According to the phasor relationship, the relationship between the instantaneous frequency and the instantaneous phase is:
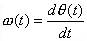
which is
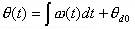
(8-4-4)
Then, the instantaneous phase difference θd is
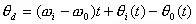
(8-4-5)
To differentiate between the two sides, the relationship between the frequency differences is
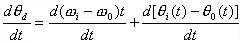
(8-4-6)
The above equation is equal to zero, indicating that the phase-locked loop enters the state of phase lock. At this time, the frequency and phase of the output and input signals remain constant, and uc(t) is a constant value. When the above formula is not equal to zero, it indicates that the phase of the phase-locked loop is not locked, the frequency of the input signal and the output signal are not equal, and uc(t) changes with time.
Since the voltage control characteristic of the voltage controlled oscillator is as shown in Fig. 8-4-3, this characteristic indicates that the oscillation frequency ωu of the voltage controlled oscillator is centered on ω0 and varies with the change of the input signal voltage uc(t). The expression for this attribute is
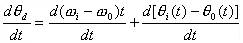
(8-4-6)
The above formula shows that when uc(t) changes with time, the oscillation frequency ωu of the voltage-controlled oscillator also changes with time. The phase-locked loop enters the “frequency pullâ€, and the frequency of the input signal is automatically tracked to make the phase-locked loop enter. Locked state and keep the state of ω0=ωi unchanged.
Phase-locked loop application
1. Application of phase-locked loop in modulation and demodulation
(1) The concept of modulation and demodulation
In order to realize the long-distance transmission of information, the signal is modulated by the modulation method at the transmitting end, and the receiving end must perform demodulation after receiving the signal to restore the original signal.
The so-called modulation is to control the parameters of the carrier signal uC by using the input signal ui carrying the information, so that a certain parameter of the carrier signal changes with the change of the input signal. The parameters of the carrier signal are amplitude, frequency and phase. Therefore, the modulation has three kinds of amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM).
The characteristic of the amplitude modulation wave is that the frequency is equal to the frequency of the carrier signal, and the amplitude varies with the amplitude of the input signal; the characteristic of the frequency modulation wave is that the amplitude is equal to the amplitude of the carrier signal, and the frequency varies with the amplitude of the input signal; the phase modulation wave The characteristic is that the amplitude is equal to the amplitude of the carrier signal, and the phase varies with the amplitude of the input signal. The schematic diagram of the amplitude modulation wave and the frequency modulation wave is shown in Fig. 8-4-4.
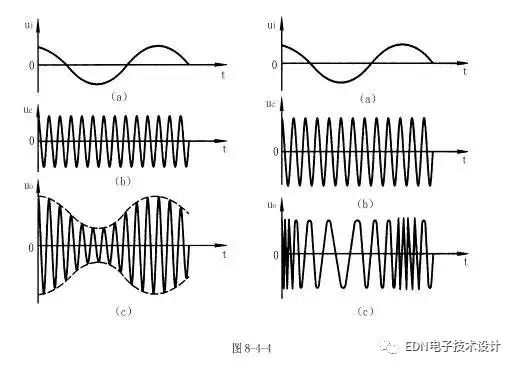
(a) in the above figure is an input signal, also called a modulation signal; (b) is a carrier signal, and (c) is an amplitude modulation wave and a frequency modulation wave signal.
Demodulation is the inverse of modulation, which reduces the modulated wave uO to the original signal ui.
2. Application of phase-locked loop in frequency modulation and demodulation circuits
The characteristic of a frequency modulated wave is that the frequency varies with the amplitude of the modulated signal. As can be seen from the 8-4-6 equation, the oscillation frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator depends on the amplitude of the input voltage. When the frequency of the carrier signal is equal to the natural oscillation frequency ω0 of the phase locked loop, the frequency of the output signal of the voltage controlled oscillator will remain unchanged at ω0. If the input signal of the voltage controlled oscillator has the signal uc output from the phase-locked loop low-pass filter, and the modulation signal ui, the frequency of the output signal of the voltage-controlled oscillator is centered on ω0, which varies with the amplitude of the modulated signal. And the changing FM signal. Therefore, the FM circuit can be composed of a phase-locked loop, and the block diagram of the FM circuit composed of the phase-locked loop is shown in Figure 8-4-5.
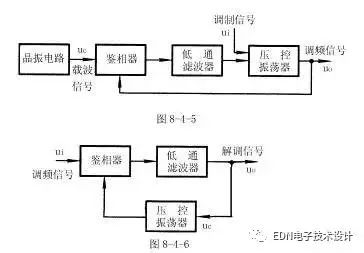
According to the working principle of the phase-locked loop and the characteristics of the FM wave, the block diagram of the demodulation circuit is shown in Figure 8-4-6.
3. Application of phase-locked loop in frequency synthesis circuit
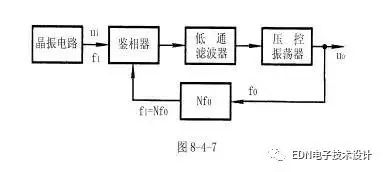
In modern electronic technology, in order to obtain a high-accuracy oscillation frequency, a quartz crystal oscillator is usually employed. However, the frequency of the quartz crystal oscillator is not easy to change, and the frequency synthesis technology such as phase-locked loop, frequency multiplication, frequency division, etc. can be used to obtain multi-frequency, high-stability oscillation signal output.
The output signal frequency is larger than the crystal signal frequency, which is called the phase-locked frequency multiplier circuit; the output signal frequency is smaller than the crystal signal frequency, which is called the phase-locked frequency divider circuit. The block diagram of the phase-locked multiplier and phase-locked frequency division circuit is shown in Figure 8-4-7.
Product categories of Cloth Pen Nib, it is belong to Passive Stylus Pen. Passive stylus pen is characterized by being cheap and without charging. But compared with the active capacitive stylus pen, its tip diameter is larger, so it cannot be used in works with high precision. Using high-quality conductive cloth head, smooth contact with the screen.
Cloth Pen Nib,Multi-Functional Pen Stylus Pen,Stylus Pencil With Clip,Touch Stylus Pencil
Shenzhen Ruidian Technology CO., Ltd , https://www.szwisonen.com