With the continuous improvement of modern electrification, people are increasingly demanding the quality of power distribution. At present, although various types of voltage regulators are gradually being upgraded, they still do not block the vandalism of harmonics; on the contrary, the harmonic hazards that follow are becoming more and more important. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct qualitative analysis on the generation and harm of harmonics in order to deepen understanding and discard both, and to fully exert its advantageous aspects while suppressing harmonic hazards.
1 Harmonic hazardHarmonic hazards should be discussed from China's power distribution system. China has always adopted the 50Hz AC power supply system. In the process of voltage regulation protection, harmonic hazards are rarely considered. This provides conditions for the generation and continuation of harmonics, which cause harmonic interactions, which on the one hand damages the appliance and on the other hand consumes a large amount of electrical energy. Table 1 shows the classification of positive, negative and zero sequence harmonics in a 50 Hz AC power supply system.
Table 1 Harmonic classification
Harmonic number 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Frequency (Hz) 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
Phase sequence - 0 + - 0 + - 0 +
It is precisely because of the existence of various harmonics that the 50Hz sinusoidal alternating current waveform distortion causes normal operation. In the three-phase four-wire power supply transformer, three times the harmonic multiplication of integer multiples is superimposed to the primary side of the transformer, causing the coil to overheat, and at the same time causing the neutral current to be too large, heat, or even burnt out. During the operation of the motor, the harmonics severely distort the AC voltage waveform and burn out the motor. In the reactive power compensation circuit, harmonics form resonance and burn out the capacitor cabinet. In daily life, the fluorescent tube is burned out, and the starter cannot be started, etc., which are caused by harmonics.
In addition to causing damage to the circuit, the presence of harmonics also limits the increase in power distribution factor. When the power factor is increased by the capacitor compensation circuit, the negative influence of harmonics is inevitably brought about. If the number of harmonics is high, the reactive compensation capacitor is likely to be broken down.
Qualitative analysis of 2 harmonicsThe role of each harmonic in the circuit is different. Now the qualitative analysis of the two common effects of harmonics is carried out to find out the cause and suppress it.
2.1 Superposition characteristics of harmonics
The superposition of harmonics is related to the phase sequence. In the same circuit, some harmonics interact with each other or cancel each other out, but more occasions often overlap each other, causing significant distortion of the waveform. For example, when only 3 harmonics appear, the waveform is shown in Figure 1. When the 3rd and 5th harmonics appear at the same time, the sine wave changes significantly, as shown in Figure 2.
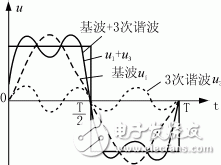
Figure 1u1, u3 and their superimposed waveforms
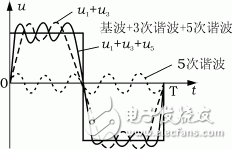
Figure 2u1, u3, u5 and their superimposed waveforms
If you continue to superimpose, the sine wave will undergo a qualitative change. The square wave can be expanded by the following equation using the Fourier series.
Ui=4Um[sin2Ï€ft+(sin6Ï€ft)/3+(sin10Ï€ft)/5
+...+(sin2kπft)/k〗/π(1)
Where ui is the voltage after superposition, Um is the fundamental amplitude, f is the frequency of the fundamental wave 50 Hz, and k=1, 3, 5... is an odd number.
Of course, there are many other types of harmonic superposition, such as sawtooth waves contain a series of even harmonics (see Figure 3).

Figure 3 sawtooth waveform
Its Fourier series expression is
Ui=A/2-A[sin2πft+(sin4πft)/2+(sin6πft)/3+...(sin2kπft)/k〗/π(2)
Where ui is the voltage after superposition, A is the amplitude of the sawtooth voltage, f is the fundamental frequency of 50 Hz, and k is a natural number.
It can be seen from the above analysis that the superposition of harmonics is not negligible, which is most evident in the three-phase four-wire power supply system. Since the harmonics are superimposed on each other, the neutral line will heat up due to excessive current, as shown in Figure 4. In addition, the phenomenon that the neutral busbar and the terminal block in the distribution line are overloaded and overheated is also caused by harmonic superposition.
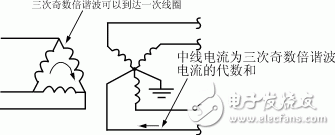
Figure 4: The neutral current in the three-phase four-wire power supply system
2.2 Characteristics of higher harmonics
The higher harmonics are also the same as the fundamental wave. The low impedance path is always selected, but unlike the fundamental wave, the higher harmonics preferentially select the capacitive circuit. Because the capacitor has the characteristics of high frequency blocking low frequency. It can be analyzed by the mathematical expression Xc=1/2Ï€fC. The magnitude of the reactance Xc in the harmonic circuit is inversely proportional to the product of the harmonic frequency f and the capacitance capacity C. Therefore, the higher the harmonic frequency, the smaller the capacitive reactance Xc, the harmonic current The bigger the harm, the greater the harm. This is most evident in the reactive compensation circuit. If you do not pay attention to the analysis and measurement of the harmonic content, and rely solely on reactive power compensation to improve the power factor, the higher harmonics will burn out the compensation capacitor. In addition, the harmfulness of higher harmonics, a common example in daily life is the long life of the fluorescent lamp and the damage of the starter.
Celeron Mini Pc,Office Mini Pc,Mini Desktop,Linux Mini Pc
Shenzhen Innovative Cloud Computer Co., Ltd , https://www.xcypc.com