A PA system is usually a system that amplifies the speaker's voice in real time to the listener. The speaker and the listener are usually in the same acoustic environment. A successful sound reinforcement system must have sufficient loudness (sufficient sound gain) and sufficient sharpness (low percentage of speech intelligibility loss) and can evenly cover the audience without covering the area without the listener. .
The sound reinforcement system consists of a sound reinforcement device and a sound field, mainly including the sound source and the acoustic environment surrounding it, a microphone that converts the sound into an electric signal, a device that amplifies the signal and processes the signal, a transmission line, and a speaker that converts the signal into an acoustic signal. And the acoustic environment of the audience area.
Sound reinforcement system classification (1) Classified by work1. The sound reinforcement system: The microphone and the speaker are in the same sound field, and there are conditions for acoustic feedback self-excitation, and the gain of the sound transmission is limited.
2. Reverberation system: Only sound sources such as decks and CD players do not have acoustic feedback conditions, which is a special case of the sound reinforcement system.
(B) Classification by purpose1. Outdoor sound reinforcement systems: stadiums, art squares, musical fountains, large-scale mobile performances, etc.
Features:
The space is wide, the service area is large, the background noise is large, and it is affected by the reflection of the surrounding buildings. Mainly direct sound, non-reverberation sound, when the reflection sound delay exceeds 50ms (17m), there will be heavy sound or echo, affecting sound clarity and sound image localization. Sound effects (especially musical fountains) are also affected by weather conditions, disturbances and environmental disturbances.
2. Indoor sound reinforcement system: all kinds of theaters, stadiums, dance halls and so on.
Features:
Professionalism is very strong. The system configuration is different depending on the function. The sound conditions have a great influence on the sound effects.
3. Mobile performance system: commonly used for large-scale performances, temporary installation system.
Features:
Audio equipment must be compact, easy to transport and install, and the use of harsh environments. Large system investment.
4. Public Broadcasting System (PA): Stations, airports, subways, ports, schools, hotels for broadcast programs and background music and also serve as fire emergency broadcasts.
Features:
Use a lot of functions, acoustic requirements are not harsh, transmission distance, using constant voltage transmission.
5. Conference system: conference center, telephone conference, video conference and digital conference system.
Features:
Improve the efficiency of the conference, with clear voice, no confusion, and multiple functions (conference discussion system, voting system, simultaneous interpretation system, etc., including video synchronization recording and conference delegate identification, etc.).
1. Frequency response: Is the system playback sound within the expected frequency range and expected deviation?
2. Power processing: Can the system handle the power required without distortion or damage to the equipment?
3, Coverage: Does the system replay sound All frequencies can cover all listening areas?
4. Subjective quality: Can the system meet the design criteria?
5. Stability: Is the system stable?
6. Noise: Is there unnecessary noise in the system?
Steps to measure and optimize the sound reinforcement systemFor the measurement and optimization of sound reinforcement systems, each person's method steps may be very different, but generally can be summarized as the steps shown in Figure 1:

This section mainly describes the three major measurement steps of frequency division setting, delay setting, and equalization compensation.
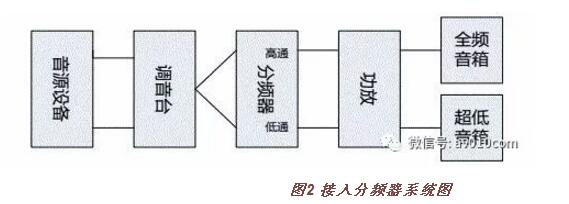
Loudspeaker system speakers generally include subwoofers and full-range loudspeakers. Any one loudspeaker can not perfectly reproduce all frequency bands in the audio signal. The subwoofer reproduces the lower-frequency part of the audio and cannot be represented. The high-frequency band in the audio; the bass performance of the full-range speaker is insufficient. While the input signal is a full audio signal, the low-frequency components of the ultra-low sound box can not normally be restored to sounds for the low-frequency components of the full-range sound box. The speaker is an energy conversion device. These components that cannot be restored to sound are mostly converted into heat energy in the speaker. This not only does not allow the speaker performance to be fully exerted, the effect is not good, and the speaker may be damaged. Many components of the speaker unit in the speaker are glued together, and the heat resistance of various glues is limited. When the speaker cannot convert the input audio signal into sound, the speaker unit converts this part of the electric energy into heat energy. Because of the closed structure of the speaker and the limited space in the box, the heat dissipation will not be very good, and these heat energy will continuously accumulate in the box, resulting in As the temperature continues to rise, once the temperature of the horn unit exceeds the heat-resistant temperature of the glue, structural damage to the horn unit will result.
The electronic frequency divider is a sound processing device that divides a full-band audio signal into two or more parts. It is composed of an internal high-pass filter circuit and a low-pass filter circuit, which can cut the full-band audio signal into two or three parts according to the needs of the system. The high-pass filter is used to control the lower limit of the signal, so that signals of other frequencies higher than a set frequency value pass, and signals lower than the frequency value are filtered by attenuation; the low-pass filter is opposite to the high-pass filter. This is used to control the upper limit of the signal, allowing other frequency signals below this set frequency value to pass, and signals above this frequency value are filtered for attenuation. With the electronic crossover device, the system can be optimized to solve the above problems. The full-band audio signal is divided into two channels into the divider, and the one-way divider high-pass filter output is connected to the amplifier and then the full-range speaker, and the other filter low-pass filter output is connected to the amplifier and then the full-range speaker. (Figure 2)
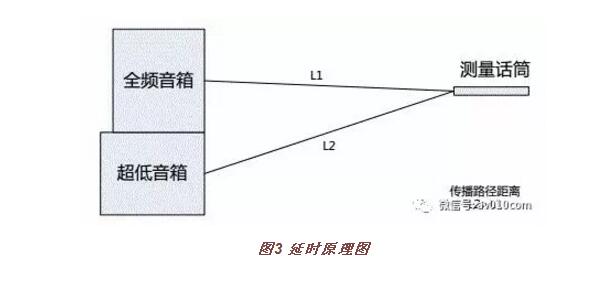
2, delay setting
Acoustic waves are transmitted in the form of alternating positive and negative changes. This alternating positive and negative changes are related to the propagation time of the sound waves. This concept of positive and negative is what we call phase. The sound reinforcement system will appear different degrees of phase distortion during the playback of the audio signal. Two loudspeakers in the sound reinforcement system may have different time when they reach the same listening point due to different placement positions, different structures, and differences in speaker energy conversion time. (Figure 3)
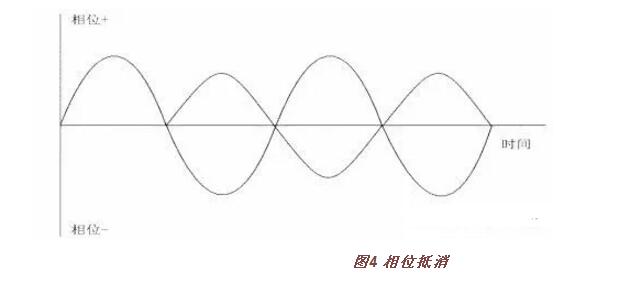
The time difference leads to the interference of sound waves, which directly affects the quality of listening. For example, sound waves from one speaker reach a certain point is positive, and sound waves from another speaker arrive at the same point later than the first point and may become negative phase. At this time, the positive and negative offsets occur, and the sound energy is lost. (Figure 4)
Therefore, we need to adjust the speaker delay when debugging and optimizing the system. In order to solve this problem, we must know how long the two loudspeakers replay the signal relative to the reference signal. The difference in this time is generally milliseconds. The human ear cannot recognize it alone. This requires measurement. Tools for accurate measurements. Then delay the relatively advanced signal. The delayer is a device that stores the input signal first and then outputs it according to the set time through the internal storage circuit. Using the delayer, we can debug the system delay.
3, balance compensation
In the measurement of the frequency response of the sound reinforcement system, the measurement signal of the average energy of the entire frequency band from 20 to 20000 Hz from low to high is sent to the sound system, and the output spectrum will be found to have different degrees of distortion. The causes of these distortions are acoustic factors and environmental factors.
Since the speakers can't be reduced by one hundred percent when they restore audio signals, there are always more or less defects.
At the same listening position, one can hear the direct sound from the speakers and the reflected sound reflected from the reflecting surface. (Figure 5)
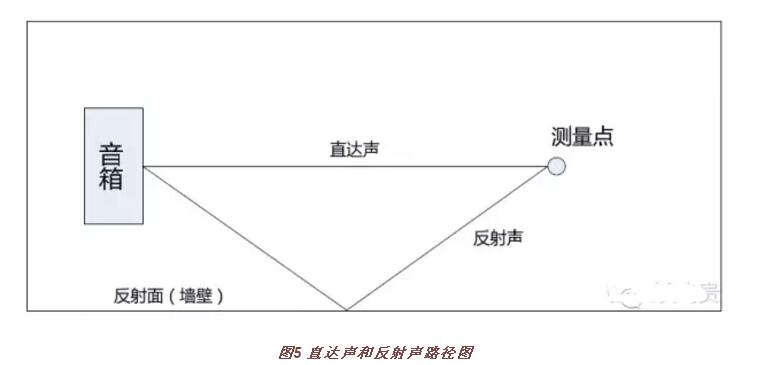
Since the direct and reflected sounds arrive at the same listening point with different paths, the distances to reach the listening point are different, resulting in time difference between the direct sound and the reflected sound arriving at the listening point, and phase differences may occur. If the direct sound and the reflected sound of different frequencies have different phases, then some of the energy will be cancelled out and there will be spectral depressions, that is, valleys. If the direct and reflected sounds of some frequencies reach the same phase in the same point, then the energy will be superimposed and the spectrum will appear to be convex, that is, the peak. The existence of peaks and troughs in the spectral characteristics makes the quality of listening much less favorable. We need to cut down the peaks, fill in the valleys, and distort the spectrum of the sound reinforcement system as little as possible.
We can use the equalizer to amplify and adjust the electrical signals of various frequency components to compensate for the speaker's own playback distortion and sound field defects and achieve equalization compensation.
Teaching and training meetings, classroom teaching; traditional projectors are not easy to carry. In school classrooms, due to the naughty students, projectors are not safe in the classroom and are easily damaged by students. The portability of micro projectors makes up for the teaching vacancies. In the future, teachers will give lectures. You only need to store the data in the projector to show it to students for teaching, saving the trouble of textbooks and handwriting with pens and chalks.
portable projector for teaching,portable projector education,portable classroom projector,projector for teachers
Shenzhen Happybate Trading Co.,LTD , https://www.happybateprojector.com