Summary:Based on open source mobile terminal operating system Android developed a video player video player consists of file browser, video playback, audio playback, playlist management and lyrics synchronization display modules, the interface is generated using XML script configuration. The software implements the management of the media library based on the file browser, which greatly facilitates the user's operation software to scan the storage device every time it starts, and saves the scanned lyric file information into the lyric database. For the song being played, the lyric file is retrieved according to the song name, and the lyrics are displayed simultaneously. The player was functionally tested and verified on the Android emulator and the 0MAP 3530 development board.
Keywords: Android; video player; lyrics display; 0MAP3530
0 Preface
The original meaning of the word Android refers to "robot", which is also the name of the open source mobile terminal operating system based on Linux platform announced by Google on November 5, 2007. The platform consists of operating system, middleware, user interface and application software. It is the first truly open and complete mobile software for mobile devices.
With the continuous development of technology, mobile phones are no longer just mobile communication tools for people's daily life, but a multimedia platform that can provide powerful multimedia functions. More and more people like to use mobile phones to listen to music and watch movies.
The music player built into the Android system manages songs based on the media library, and does not support simultaneous display of lyrics. For some users who are used to the file browser-based player, it is inconvenient to operate. For the Android mobile operating system, you can take advantage of its rich programmable scalability to develop new player applications.
1 Android platform
Related technologies related to Android software development include Android SDK (development plug-in, debugging toolkit, etc.), Android system architecture and Android application components.
1.1 Android SDK
The Android SDK (Software Development Kit) provides API interfaces and tools for Android application development using the Java language on the Android platform. Among them, the most important tools are Android emulator and Eclipsel2 Android development tool plug-in, and the SDK also contains various tools for debugging, packaging and installation on the emulator.
The Eclipse IDE's Android Development Tools Plugin for the Eclipse IDE (ADT) greatly extends the Eclipse integrated environment capabilities, making it easy and fast to generate and debug Android applications. With Eclipse, the ADT plugin speeds up the development of Android apps.
The Android emulator is a virtual mobile device running on a computer that can be used to simulate, design, debug, and test an application using a simulator to simulate an actual Android runtime environment.
The Dalvik Debug Monitor Service (DDMS) integrates Dalvik (a virtual machine (VM) customized for the Android platform) that manages processes and assists debugging on the emulator or device. DDMS provides process management, generates trace data, observes heap and thread information, intercepts simulator screens, and simulates incoming calls or text messages.
1.2 Android system architecture
Android is a software set specifically for mobile devices, which includes an operating system, middleware and some important applications].
Android's system architecture from top to bottom is the application, application framework and components, Android runtime library and other libraries, optimized Linux kernel [.
1.3 Android application components
The operating environment of a mobile phone is relatively complicated, and a program often runs with many unexpected situations, such as an incoming call or a short message and insufficient power. These issues have solutions in Android. In Android apps, the following components are especially important:
(1) Activity as the name suggests, Activity is the activity. The application must contain at least one Activity. Activity provides a virtual user interface, each Activity has a default window that can be used to display the user interface. In general, it is a full-screen window. For example, each user interface of the video playback software is an Activity.
(2) The main difference between ServiceService and Activity is that Service is active in the background, it has no user interface]. A typical application scenario is that after the user selects a playlist to start playing, he or she leaves the user interface (Activity). If you still want the song to not pause, you can use the Service to call the player instead of calling the player in the Activity. .
(3) Intent In Android, each behavior can be abstracted as an Intent. You can simply understand an Intent as a message that contains data. Intent can be used to start an Activity or Service, which can be used for communication between processes. In fact, the launch of the application is also implemented through the Intent.
(4) Content providers Android platform has a set of SQLite data storage mechanism built in, and contains a series of related methods to manage SQLite Database _7].
In the application, you can access the database through Content providers. Each Content provider defines a set of methods for accessing its corresponding database. When the application is newly created, the application can also define the corresponding Content provider to share data with other applications. In general, the application does not directly call the function defined by the Content provider, but indirectly through ContentResolve. The advantage of this design is that a ContentResolver can access any Content provider and unify the interface.
2 hardware platform
The system's hardware platform uses the OMAP3530-based development board DevKit8000. TI's OMAP3530 application processor _8 integrates a 600 MHz ARM Cortex-A8 CPU core and a 430 MHz C64x+ DSP core, and provides a rich peripheral interface such as USB 2.0OTG, SD/MMC and LCD. For a variety of wireless handheld applications. The DevKit8000 development board is externally connected to a 4.3-inch LCD screen, resistive touch screen and audio input/output interface, which can be used to develop Android-based video players.
By patching the package and developing peripheral drivers such as LCD drivers, touch screen drivers, and button drivers, the Linux kernel version 6.2.29 and the Android system version 1.6 were ported on the DevKit8000 development board.
3 Android video player software development
3.1 Software features
Android video and audio playback software mainly includes the following features:
(1) Play video supports fast forward, rewind, pause, resume and progress drag.
(2) Play audio support fast forward, fast rewind, previous, next, pause, continue, stop and progress drag; support random play, loop play two modes; support lyrics synchronous display.
3.2 Relationship between modules
The audio and video playback software project files mainly include src folder (Java source code), res folder (resource file) and AndroidManifest. Xml (program list). The software is mainly composed of 8 Activities, and each Activity corresponds to one module. Different Activities communicate and call each other through In-tent.
The relationship between the various modules is shown in Figure 1.
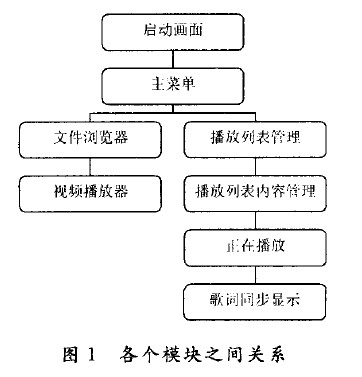
The order in which the video playback is called is <Startup Screen>, <Main Menu>, <File Browser>, <Video Player>; the order in which the audio playback is called is <Startup Screen>, <Main Menu>, <Playlist Management>, <Playlist Content Management>, <Playing>. On the <Now Playing> interface, click the corresponding button to execute the lyrics synchronization display function.
AndroidManifest in the project directory: In the xml (list file), add a description of each activity. The following is a description of the corresponding splash screen:

3.3 Software Module
According to the video playback software function, the software can be divided into the following modules:
(1) <Startup Screen> module. The main function is to display the software startup screen. The timer thread is used to control the startup screen display time, and when the user presses the button, the startup screen display is immediately interrupted and jumps to the <Main Menu> module.
(2) <Main Menu> module. The main function is to provide a user interface for the playback software. The user interface is generated by the XML configuration of Android.
The main menu provides three options, namely video playback, audio playback and exit program; when the video is playing, the <File Browser> module is called to let the user select the video file to be played. When playing audio, call the <Playlist Management> module to let the user select the list that needs to be played.
(3) <File Browser> module. Used to browse files on the memory card. If the path is a folder, all the files under the folder are listed; if the path is a file, first check whether the file extension is a supported video format, and if so, call the built-in player to play.
(4) <Audio Playback> module. It includes the following modules:
1 <Playlist Management> module. The main function is to add, delete, and rename lists. Access the system's playlist database through Content providers and update the database with the modified results. Because it uses the system's database, it is shared with the built-in music player list. It also provides an interface to add list content. Go to the <Playlist Content Management> module through the playlist management module.
2 <Playlist Content Management> module. The main function is to add, delete, and multi-select songs in the playlist. In Android, each list will have a corresponding list content library, which saves the song ID contained in the list. It can be accessed and modified through Content Providers. Among them, the add function is implemented based on the file browser, and the music file can be marked and added in the file browser.
3 <Now Playing> module. The main function is to display the related information of the song (album cover, album name, singer, length, etc.) and display the time progress of the song being played, and control the playback of the song.
The interface of the <Now Playing> module is generated using the XML configuration.

The Android's music library has parsed the song's Idv2 or Idv3 tags and saved the song's related information (including singer, genre, duration, etc.) in the media database. You only need to access the database through Contenttent providers, you can get the relevant information and send it to display. The program source code for getting song related information is as follows:


By creating a MediaPlayer player class object, the API provided by An-droid can be used to decode and play the file.
4 <Lyric Synchronization Display> module. When the program starts, the memory card is scanned, and the scanned lyric file name and path are saved to the lyric database. For the song being played, the lyric file is automatically retrieved according to the song name, and the lyrics are displayed simultaneously. The first time you start the program, you need to create a new lyrics database to save the lyrics file information. An-droid provides the class SQLiteOpenHelper for creating new databases.
DATABASE—CREATE is a string macro of a SQL primitive whose content is “create table lyric—meta (an id integer primary key autoincrement, a display— nam e text notnull, a data text not nul1);†means creating a lyric file The table contains an id, a display_name, and a data three column. Where jd is a self-incrementing and unique integer, a display-name is the name of the lyric file, and a data is the path of the lyric file.
4 system test
First, debug and test the functions of the video player on the simulator of Android SDK 1.6. After debugging, copy the compiled installation file (.APK) to the SD card, use the Android file manager to install the player software to the OMAP3530 development board system, and then test the video files, MP3 music files and corresponding The lyrics file (.1rc) is copied to the SD card. The audio and video player on the 0MAP3530 development board can select the audio and video files through the file browser and play normally. When playing the audio file, the matching lyrics can be displayed normally, which supports fast forward and fast. Control functions such as back and pause.
5 Conclusion
This article takes the development of audio and video player on Android as an example, and gives the development method of the application on Android in detail. The developed audio and video player was tested on the Android phone simulator and the OMAP3530 development board.
Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire
| About Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire |
Fiber Glass Covered Aluminum/Copper Wire is according to customers` requirement, aluminum/Copper conductor is evenly covered with one or two layers of non-alkali fiberglass, then it`s impregnated in compatible insulating coating of required thermal class baked to make a whole between fiberglass and aluminum/Copper conductor
Excellent resistance to abrasion and solvent, excellent electricity

a) Excellent resistance to abrasion and solvent,
b) Excellent electricity performance
c) Excellent heat shock, adherence and flexibility,
d) High cut through
e) Resistance to high voltage in oil;
f) Rise up the filling coefficient of the transformer;
g) Reduce volume and the cost of the transformer
Glass Covered Winding Wire,Glass Fiber Covered Flat Copper Wire,Fiber Glass Covered Copper Wire,Generator Flat Glass Fiber Covered
HENAN HUAYANG ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GROUP CO.,LTD , https://www.huaonwire.com