The Bluetooth Technology Alliance announced the launch of Bluetooth 5.0 as one of the biggest events in the Internet of Things in 2016. Lei Feng.com has previously detailed the features of Bluetooth 5.0, including its amazing four times the connection distance and twice the transmission speed. Such a huge increase naturally has its strategic intent - the battle against Wi-Fi as the throne of the Internet of Things wireless data transmission protocol.
Previously, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi can be said to have their own advantages: Bluetooth has lower power consumption, smaller size and lower cost, and is suitable for short-distance data transmission between several devices; Wi-Fi is characterized by high bandwidth and long distance. More connected devices (different routers have different upper limit on the number of connected devices), suitable for large-scale, large-scale data transmission and signal coverage.
However, with the popularity of the Internet of Things, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have been upgraded one after another, both of which went to the same battlefield - Bluetooth upgrade to version 5.0, increasing bandwidth and transmission range; Wi-Fi launched "Wi-Fi HaLow" to reduce power consumption Battery life. The discerning eye can see that the direction of the two upgrades is the other party's expertise - which means that the functional positioning is coincident, and they will undoubtedly compete in the consumer and enterprise-level IoT market.

Family Internet of Things
Bluetooth 5.0 enhanced signal coverage - claims to cover the entire apartment, which is comparable to the data transmission distance of home Wi-Fi routers, compared to the rapidly popular 5GHz home Wi-Fi, if you only look at this Parameters, in the application of home Internet of Things devices, the two have officially stood at the same level.
It should be noted that since Bluetooth uses the 2.4GHz band, in order to reduce signal interference, more users are likely to choose Wi-Fi in the 5GHz band instead of 2.4GHz. But Bluetooth 5.0 is better than the transmission distance. Therefore, in the future of home Internet of Things devices, there is a possibility that users will use Wi-Fi for devices (mobile phones, computers, etc.) that require large data traffic, while other smart home devices use Bluetooth.

Of course, there are two issues involved here:
Users using 2.4GHz Wi-Fi will deprecate Bluetooth 5.0 due to signal interference risk;
Commercially available Wi-Fi has a signal relay amplifier (or booster) that allows users to save the country by curve, enhance Wi-Fi signals, and cover the entire apartment. Let's see how the Bluetooth Technology Alliance solves the above problems:
At the time of the release of Bluetooth 5.0, the Bluetooth Technology Alliance stated that the new version of Bluetooth has stronger anti-interference ability, especially for Wi-Fi and LTE signals, which can avoid "signal congestion" in a limited space to a certain extent.
The development of the Internet of Things mesh networking technology (mesh networking) technology. This technology enables Bluetooth devices to act as signal relays to each other and to transmit signals farther.

In fact, with a mesh network, each Bluetooth IoT device is equivalent to a signal-relay amplifier from another device. It is worth noting that:
It is not known when the technology will be commercialized, and it is expected that it will be hoped in the short to medium term.
The cost is unknown. This will directly affect whether IoT devices on the market will support it. If most don't support it, its effect is small.
Mesh technology is not limited to Bluetooth, but is theoretically applicable to Wi-Fi and cell phone signals. Enterprise Internet of Things
Consumer domain (family) IoT devices are a big battleground for Bluetooth 5.0 and Wi-Fi in the future, and are evenly matched. In the enterprise Internet of Things market, Bluetooth has even achieved a first-mover advantage.
This is mainly reflected in two aspects:
According to market research by third-party organizations, Bluetooth has become the most popular IoT wireless protocol (as shown below), while the Wi-Fi market share is far behind. The third place is the specialized IoT wireless standard Zigbee. .
In addition, products with Bluetooth 5.0 will be released in 2017, and Wi-Fi HaLow for the enterprise Internet of Things market is expected to be released at 2018.
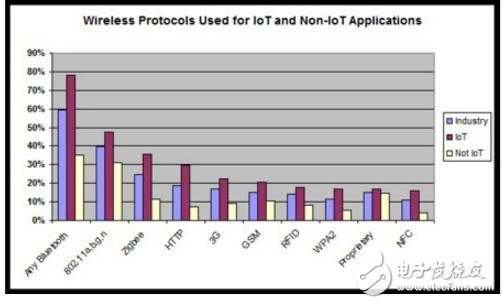
Table 1: Application of each wireless transmission protocol in the Internet of Things (red bars) and non-Internet of Things (yellow stripes). Violet for industrial applications (Source: iot technews)
Bluetooth is currently leading, relying mainly on its small size and energy consumption advantages. Quite a lot of IoT devices, such as sensors and wearables, are very small, and their battery capacity is very limited, and repeated charging is a very troublesome thing for us humans. The Bluetooth receiver is small and saves 25% to 2x compared to Wi-Fi devices – a key for small IoT devices without an external power supply.

For this Bluetooth 5.0, the Bluetooth Technology Alliance did not disclose its energy consumption. However, most people in the industry are optimistic that it is not much different from the existing Bluetooth 4.2 power consumption, and even optimized.
On the Wi-Fi side, the new Wi-Fi HaLow uses a 900 MHz signal frequency to dramatically reduce power consumption and adds a “sleep mode†to further extend the life of the device. In addition, lower frequencies also provide better wall penetration and further increase signal coverage. It can be seen that Wi-Fi HaLow's advantage in IoT devices is not lost to Bluetooth. If it is successfully popularized, the number of wins and losses is likely to be reversed. However, Wi-Fi HaLow currently has several challenges:
The progress is slow and is still in the standard setting stage. As for whether it can be released on time in 2018, it is still unknown.
Data packaging in the 900 MHz band is unique and requires an additional infrastructure that is not compatible with existing Wi-Fi networks. This means that companies need to update their devices to manage Wi-Fi HaLow.
In some countries in Europe, Asia and Australia, 900 MHz is not open to civilian applications. However, the launch of the new version is not just Wi-Fi. In fact, Bluetooth has two versions: the "classic" classic version with relatively high energy consumption but better effect; and the "BLE" version with low power consumption - most of the smartphones use this version. The timely launch of Bluetooth 5.0 provides a combination of better transmission speed, distance, power consumption and cost. According to Lei Feng.com, Bluetooth 5.0 is equivalent to the energy consumption of the "BLE" version and the effect of the classic version, which means a better energy consumption ratio. Whether this is the case or not, it is still waiting for the product to be tested after its launch.
Therefore, Bluetooth will continue to lead the IoT market in the expected time. The picture below shows the wireless solutions developers are expected to adopt in the next 12 months:
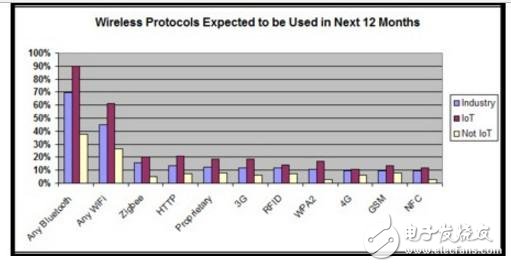
Table 2: Developers expect to adopt each wireless transmission protocol in the next 12 months. Internet of Things (red bars), non-Internet of Things (yellow strips), industrial applications (purple strips) (Source: iot technews)
Although Bluetooth has taken the lead, in the long run, the number of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Internet of Things is still unknown. In the end, this wireless transmission protocol century hegemony will end, we will wait and see.
Car Megaphone,Megaphone For Car,Vehicle Megaphone,Megafono Amplificador
Shangqiu Huayitong electronic technology co., Ltd. , https://www.huayitongmegaphones.com