[Source: "High-tech LED-technology and application" February issue Shi Guangdian]
LED chip, package, and application technology are progressing at an unprecedented speed. For 1.2m T8 fluorescent lamps alone, the luminous efficiency has increased from 73Lm/W (peak) in 2008 to 154.6 Lm/W (peak) at the end of 2011. The rate reached 2.11 times, not to mention the speed is amazing. So far, all the manufacturers in the LED field are still pursuing the significant improvement of photovoltaics such as light efficiency, illumination and PF value and the continuous decline of prices, in order to quickly occupy the market and replace the traditional light source to become a real lighting professional. Manufacturer, or lighting expert. As everyone knows, lighting depends not only on the illuminance of the light source itself, but also on the reflection of the light-receiving surface in the environment where the space in which the illumination is located, in order to be truly illuminated.
In terms of reflectivity, the first explanation is the unit of luminous intensity (luminance): the common unit of luminous intensity is candlelight (cd, candela), and the international standard candlelight (lcd) is defined as the ideal blackbody at platinum freezing point temperature (1769). °C) is perpendicular to the luminosity of 600,000 parts in the direction of the black body (with a surface area of ​​1 m2). Why is the environment selected for luminous intensity an ideal black body rather than an object of other colors? Because the ideal black body means that the emissivity of the object is equal to 1, the energy absorbed by the object can be completely radiated, so that the temperature is kept uniformly fixed.
In addition, it can also be defined by the law of reflection: the reflected ray and the incident ray are in the same plane and are separated on both sides of the normal, and the incident angle and the reflection are equal in magnitude and opposite in sign. When light hits the interface of different media, part of the light returns to the first medium according to the law of reflection, to prove that the reflectivity of the object can make the light energy have a greater impact on the lighting environment. That is to say, the stronger the object absorbs light or the transmitted light, the weaker the reflected light is, the darker the object looks. On the contrary, if the object absorbs light weakly, the reflected light is strong, and the object looks bright, such as a mirror.
In addition, when the surface of our object observed by the naked eye seems to be smooth, but with a magnifying glass, it will be seen that the surface is uneven, when a parallel incident light hits the rough surface. The surface will reflect the light in all directions, so the incident rays are parallel to each other. Since the normal directions of the points are inconsistent, the reflected light is randomly reflected in different directions. This reflection is called diffuse reflection. The inner wall of the integrating sphere used in the industry to test various optical parameters is to use the principle of diffuse reflection to improve data stability and repeatability.
We can use the formula to express the phenomenon that light is incident from the optically dense medium to the light-diffusing medium, and when the incident angle is greater than a certain value, the light is completely returned to the original medium at the interface of the two mediums. The incident angle at which total reflection has just occurred is the critical angle, expressed in Im.
According to the law of refraction
For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.
LED chip, package, and application technology are progressing at an unprecedented speed. For 1.2m T8 fluorescent lamps alone, the luminous efficiency has increased from 73Lm/W (peak) in 2008 to 154.6 Lm/W (peak) at the end of 2011. The rate reached 2.11 times, not to mention the speed is amazing. So far, all the manufacturers in the LED field are still pursuing the significant improvement of photovoltaics such as light efficiency, illumination and PF value and the continuous decline of prices, in order to quickly occupy the market and replace the traditional light source to become a real lighting professional. Manufacturer, or lighting expert. As everyone knows, lighting depends not only on the illuminance of the light source itself, but also on the reflection of the light-receiving surface in the environment where the space in which the illumination is located, in order to be truly illuminated.
In terms of reflectivity, the first explanation is the unit of luminous intensity (luminance): the common unit of luminous intensity is candlelight (cd, candela), and the international standard candlelight (lcd) is defined as the ideal blackbody at platinum freezing point temperature (1769). °C) is perpendicular to the luminosity of 600,000 parts in the direction of the black body (with a surface area of ​​1 m2). Why is the environment selected for luminous intensity an ideal black body rather than an object of other colors? Because the ideal black body means that the emissivity of the object is equal to 1, the energy absorbed by the object can be completely radiated, so that the temperature is kept uniformly fixed.
In addition, it can also be defined by the law of reflection: the reflected ray and the incident ray are in the same plane and are separated on both sides of the normal, and the incident angle and the reflection are equal in magnitude and opposite in sign. When light hits the interface of different media, part of the light returns to the first medium according to the law of reflection, to prove that the reflectivity of the object can make the light energy have a greater impact on the lighting environment. That is to say, the stronger the object absorbs light or the transmitted light, the weaker the reflected light is, the darker the object looks. On the contrary, if the object absorbs light weakly, the reflected light is strong, and the object looks bright, such as a mirror.
In addition, when the surface of our object observed by the naked eye seems to be smooth, but with a magnifying glass, it will be seen that the surface is uneven, when a parallel incident light hits the rough surface. The surface will reflect the light in all directions, so the incident rays are parallel to each other. Since the normal directions of the points are inconsistent, the reflected light is randomly reflected in different directions. This reflection is called diffuse reflection. The inner wall of the integrating sphere used in the industry to test various optical parameters is to use the principle of diffuse reflection to improve data stability and repeatability.
We can use the formula to express the phenomenon that light is incident from the optically dense medium to the light-diffusing medium, and when the incident angle is greater than a certain value, the light is completely returned to the original medium at the interface of the two mediums. The incident angle at which total reflection has just occurred is the critical angle, expressed in Im.
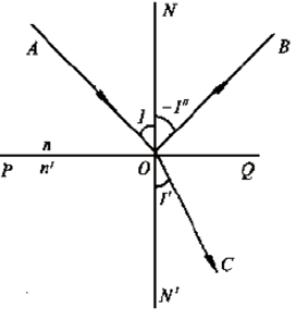
According to the law of refraction

For more information, please refer to the February issue of "High-tech LED-Technology and Applications" magazine.

Insulation Monitoring Device,Insulation Monitoring Relay,Bender Insulation Monitor,Insulation Monitor
TRANCHART Electrical and Machinery Co.,LTD , https://www.tranchart-electrical.com