Definition of harmonics
An alternating non-sinusoidal signal can be decomposed into a linear combination of sinusoidal components of different frequencies. When the frequency of the sine wave component is the same as the frequency of the original AC signal, it is called the fundamental wave. Harmonic, in a narrow sense, refers to the amount of electric current contained in the current that is an integral multiple of the fundamental wave. It generally refers to the Fourier series decomposition of the periodic non-sinusoidal electric quantity, and the rest is greater than the fundamental frequency. Electricity. Broadly speaking, since the effective component of the AC grid is a single frequency of the power frequency, any component that is different from the power frequency can be called a harmonic. When the frequency of the sine wave component is a non-integer multiple of the frequency of the original AC signal, it is called a fractional harmonic, also called a fractional harmonic or interharmonic. For any compound cycle, the vibration function y(T) is decomposed according to the Fourier series: the first term is the mean or the DC component, the second term is the fundamental or basic vibration, and the third term is the second harmonic. Analogy or after the second harmonic is collectively referred to as higher harmonics.
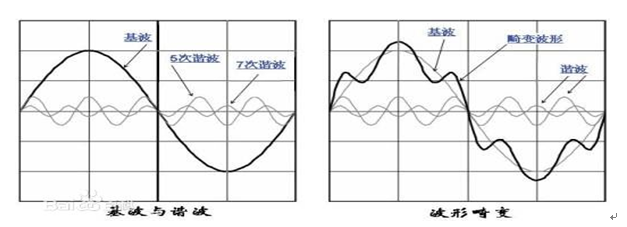
Harmonic causes
In power systems, the root cause of harmonic generation is due to non-linear loads. The main non-linear loads are UPS, switching power supply, rectifier, inverter, inverter and so on. When the current flows through the load, it does not have a linear relationship with the applied voltage, and a non-sinusoidal current is formed, that is, harmonics are generated in the circuit.
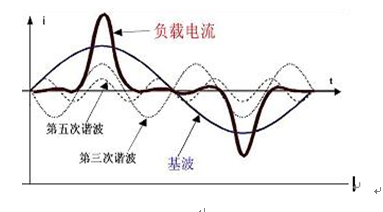
Harmonic related terms and calculation formula
1, harmonic (component) harmonic (component)
The Fourier series decomposition of the periodic AC quantity is performed to obtain a component whose frequency is greater than 1 integral multiple of the fundamental frequency.
2, harmonic order (h) harmonic order (h)
The integer ratio of the harmonic frequency to the fundamental frequency.
3, harmonic content (voltage or current) harmonic content (for voltage or current)
The amount obtained by subtracting the fundamental component from the periodic amount of alternating current. 
4, harmonic content rate harmonic raTIo (HR)
The ratio of the root mean square value of the hth harmonic component contained in the periodic AC amount to the root mean square value of the fundamental wave component (in percent), the hth harmonic voltage content rate is represented by HRUh; the hth harmonic current content rate Expressed as HRIh. 
5, the total harmonic distortion rate total harmonic distorTIon (THD)
The ratio of the root mean square value of the harmonic content in the periodic alternating current to the root mean square value of its fundamental component (expressed as a percentage). The voltage total harmonic distortion rate is expressed as THDu; the current total harmonic distortion rate is expressed as THDi. 
6, short time harmonic short duraTIon harmonics
The duration of the impact does not exceed 2 s, and the interval between the two impacts is not less than the harmonics contained in the current of 30 s and the harmonic voltage induced thereby.
National standard harmonic limit
The National Standard of the People's Republic of China GB/T 14549-1993 has clear limits on the harmonics of the utility grid.
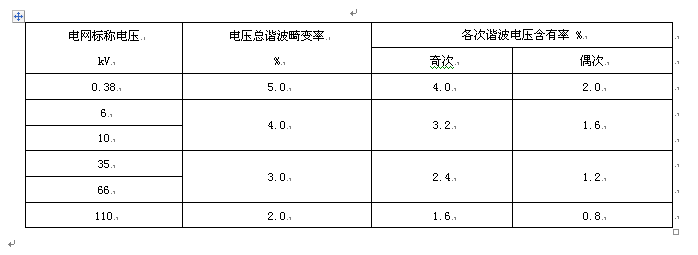
1. Harmonic voltage (phase voltage) limits of the public power grid
Table 1: Harmonic voltage of the public grid (phase voltage)
2, harmonic current allowable value
The harmonic current component (square root mean value) injected by all users of the common joint to this point shall not exceed the allowable values ​​specified in Table 2. When the minimum short-circuit capacity at the common junction is different from the reference short-circuit capacity, the conversion of the allowable values ​​of the harmonic currents in Table 2 is given in Appendix B (Supplement).
Table 2: Allowable values ​​of harmonic currents injected into common joints
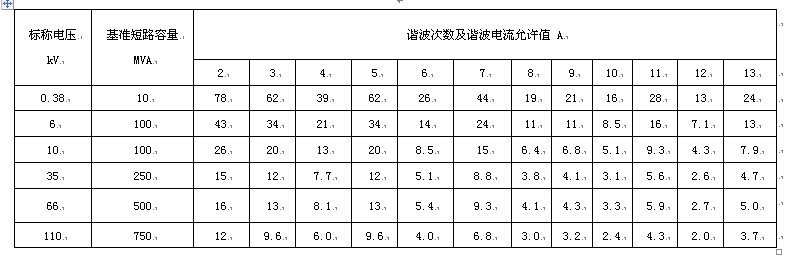
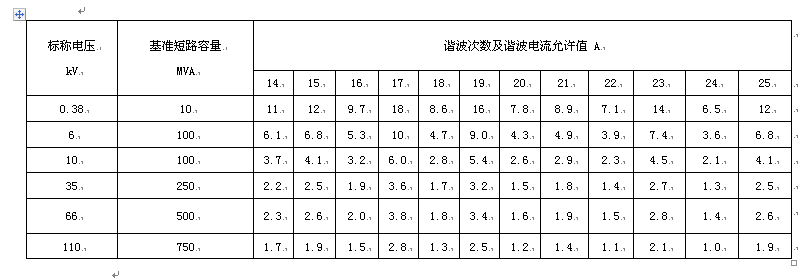
Note: The 220kV reference short-circuit capacity is 2000 MVA.
Through the above, it is not difficult to answer the questions asked by the customer. The customer's power grid is 10KV, and the measured total harmonic distortion rate of the voltage is 3.4%, then it is less than 4% according to the national standard requirement and is within the qualified range.
silicone fiberglass sleeve, silicone rubber fiberglass sleeving, silicone coated fiberglass sleeving, glass fibre sleevingfiberglass silicone sleeve
Dongguan Zhonghe Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.zhonghesleeving.com